Una foresta del 6000 a. C. sotto il mare — 6000 b.C. forest under the sea
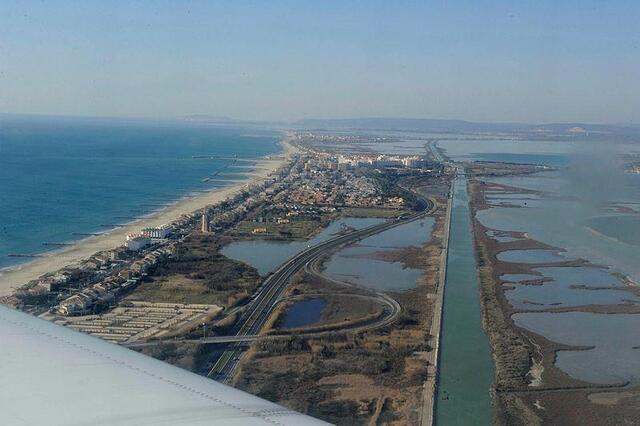
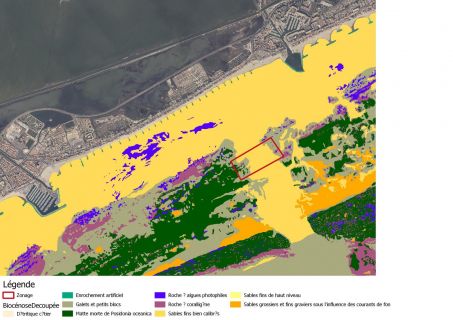

L’hanno scoperta gli scienziati del Centro di Ricerca archeologica subacquea della Linguadooca a circa un chilometro dalla costa di Palavas-les-Flots. È una foresta sommersa da 8000 anni. Ed è un bellissimo racconto in cui i protagonisti sono l’acqua e il tempo; non è legato al cambiamento climatico, ma è un’affascinante testimonianza dell’acqua come dimensione del tempo. La datazione al carbonio 14 è stata quindi utilizzata per stimare l’età della foresta: 6000 a.C. che, in effetti, coincide con il periodo in cui l’innalzamento del livello del mare è stato molto rapido. Esistono solo altre due altre foreste sottomarine nel mondo. La prima è stata scoperta al largo dell’Alabama (nel video), negli Stati Uniti, nel 2005, per effetto dell’uragano Katrina; la seconda, nel 2014, vicino al Galles. (Immagini tratte dal sito www.sciencesetavenir.fr)
FORESTA SOMMERSA IN FRANCIA #archeologiasubacquea #tempodacqua #thetimeofwater
Scientists from the Languedoc Underwater Archaeological Research Center discovered the forest about a kilometer from the coast of Palavas-les-Flots. It has been submerged for 8000 years. And it is a beautiful story whose protagonists are water and time; it is not linked to climate change, but it is a fascinating testimony of water as a dimension of time. Carbon 14 dating was then used to estimate the forest age: 6000 years B.C. which, in fact, coincides with the period when the sea level rise was very rapid. There are only two other underwater forests in the world. The first one was discovered off the coast of Alabama (see in the video), in the United States, in 2005, due to the effect of Hurricane Katrina; the second, in 2014, near Wales.
The carbon 14 dating carried out on these woody elements dated them to 6000 years B.C. The plants were identified as oaks by a xylological study. To date, only two other examples of drowned forests are known in the world. In Mobile, off the coast of Alabama (United States), revealed by Hurricane Katrina (in 2005) and dated 50,000 years ago; and in Wales, exposed by a storm, in 2014. These exceptional discoveries are direct indicators of the position of the palaeo-littoral as it was before the rise in sea level, during the Holocene, the geological period of the last 10,000 years. They constitute a proven marking of the localization of the coastline of the time.